The Complete Filmmaking Curriculum
Academy Award and Emmy-winning filmmakers methodically guide you through every step of the filmmaking process

Career Skills
The Academy Award and Emmy-winning filmmakers behind Steven Spielberg and James Cameron’s movies teach you the skills to build a successful career in the film industry.
Realities of the Film Industry
The entertainment industry does a great job of creating an illusion of how it operates, but how does it really work? Learn from top Hollywood filmmakers what really goes on behind the scenes, and how that impacts your career. (27:18)
Working Freelance
Learn the realities of working in a freelance-based industry, and how to survive. (26:14)
Preparing to Move to LA
Deciding to move to LA is a big decision, and in this video, you will learn how to prepare so you can hit the ground running.
Living in Los Angeles
Learn what to expect when you live here, from the best neighborhoods to managing the infamous LA traffic.
Getting Your First Job
So you moved to LA, and you’re ready to work. But how do you get your first job? Leading Hollywood filmmakers share the secrets of how to land your first job... and how to break into Hollywood. (22:54)
The Art of Networking
Like they say, it’s all who you know... and they’re right. In this module, learn the art of networking, meeting people, and navigating the treacherous waters of Hollywood. (22:17)
Making Money in Hollywood
Learn how to make a living in Hollywood, manage your money, and prepare for the ups and downs of the freelance world. (24:37)
Advice From the Pros
Dozens of successful Hollywood filmmakers share their secrets, tips, and advice on how to make it in the most competitive industry in the world. (21:13)
How to Survive in Hollywood
Breaking into the film industry as a writer is one thing - staying in it is another. Emmy-winning writer Steve Skrovan shares insights from his 30-year career on how to keep your Hollywood career alive and active. Learn common pitfalls, life balance, and how to stay relevant in one of the fastest-changing, exciting businesses in the world. (17:00)

Screenwriting
From the birth of an idea to the green light, this series takes you inside the writing process, and teaches the complete process of writing a feature-length screenplay.
Section 1: Getting Started
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
Beginning the Writing Process
Congratulations! You’re ready to start writing your movie script, but where do you start? Before we jump into developing characters and discussing story structure, you need to prepare your tools and set-up a space to work. In this lesson, we will share some tips and tricks to helping you prepare to write your screenplay.
Working with a Writing Partner
Writers rarely approach a new script alone, but working with a writing partner can introduce its own challenges. In this lesson, we will show you tips and techniques for finding and establishing a good relationship with a writing partner.
Finding Story Ideas & Inspiration
In this lesson, the writers behind dozens of TV shows and movies, including Everybody Loves Raymond and Now You See It, plus studio executives, top Hollywood agents, and the Academy Award-winning Christ Huntley who defined the Hollywood story structure teach you how to find inspiration and develop your idea. (17:36)
Developing a Marketable Idea
Movie making is one of the most expensive and time-consuming art forms, and before you embark on months, even years of work, it’s wise to research the potential audience for your movie. In this lesson, I partnered with Emmy and Academy Award-winning writers, studio executives, and screenwriting professors to reveal dozens of tips and tricks to determining the market for your story concept. (19:40)
Section 2: Story Structure
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
Beginning the Writing Process
Congratulations! You’re ready to start writing your movie script, but where do you start? Before we jump into developing characters and discussing story structure, you need to prepare your tools and set-up a space to work. In this lesson, we will share some tips and tricks to helping you prepare to write your screenplay.
Working with a Writing Partner
Writers rarely approach a new script alone, but working with a writing partner can introduce its own challenges. In this lesson, we will show you tips and techniques for finding and establishing a good relationship with a writing partner.
Finding Story Ideas & Inspiration
In this lesson, the writers behind dozens of TV shows and movies, including Everybody Loves Raymond and Now You See It, plus studio executives, top Hollywood agents, and the Academy Award-winning Christ Huntley who defined the Hollywood story structure teach you how to find inspiration and develop your idea. (17:36)
Developing a Marketable Idea
Movie making is one of the most expensive and time-consuming art forms, and before you embark on months, even years of work, it’s wise to research the potential audience for your movie. In this lesson, I partnered with Emmy and Academy Award-winning writers, studio executives, and screenwriting professors to reveal dozens of tips and tricks to determining the market for your story concept. (19:40)
Story Formats
Stories can be told in a number of different ways, and in this lesson, we’re going to look at how a story is structured in feature and short films, animation, commercials, documentaries, music videos, and corporate videos (17:18)
The 7 Plot Types
Every story that has ever been told, is being told, and will ever be told can be distilled into one of seven basic story lines. And every story is a variation of one of these plot types. In this lesson, we will explore each of these 7 plot types and how you can adapt them to your story. (20:01)
The Implication of Genre
Genre is the style that wraps around your plot structure. Each genre comes with its own story conventions, guidelines for the protagonist, scope of the antagonist, and plot structures. In this lesson, we look at the range of genres and how they impact your story and your ability to market your production. (16:40)
Three Act Structure
In this module, we’ll show you how to use the three act structure to properly pace your story, what should occur in each act, the length of each act, what happens at the beginning, middle and end of each act, and how to apply these techniques to your story. (39:00)
A-Story and Subplots
If you were to describe a movie in a few sentences, you would probably give me a great summary of the main plot of the story- “Raiders of the Lost Ark is about an archaeologist who goes in search of the Ark of the Covenant.” Or “Twilight” is about girl torn between two men – a vampire and a werewolf.” In both of these examples, you would be correct – but what you told me was what is part of what’s called the “A” plot, or the main storyline of the movie. Movies can also include several smaller stories called subplots, which help reveal character, push the story forward and ultimately support the A-plot. In this module, we’re going to look at how to effectively write both the A-plot and the subplots. (27:52)
Techniques to Improve Story Pacing
A good screenplay takes the audience on an emotional roller coaster, and one of the challenges facing each writer is how to keep the audience engaged through each and every minute of the story. In this module, learn literary techniques for maintaining strong pacing – especially through the second act. (14:39)
Techniques to Engage the Audience
Story pacing is critical to keep your audience engaged and interested in your movie. In this lesson, we’re going to reveal top literary tools you can use in your screenplay to keep people visually, emotionally, and psychologically engaged in your story. (23:11)
Watch a free lesson from this series
Section 3: Character Development
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
The Protagonist
As you’re writing your screenplay, the most important character to write is the protagonist. But you have several choices – is he also the main character? Does the protagonist change or remain steadfast? How do you write a character the audience will care about? How can flaws help the protagonist solve the story problem? Knowing the answers to these question will help you craft a compelling character, so in this module, we’re going to explore techniques for writing a strong, multi-dimensional protagonist. (25:48)
The Antagonist
The antagonist has been classically referred to as the bad guy, the villain, or the adversary. But more properly defined, he, she or it is the literary opposite of the protagonist – the character who opposes the goals of the protagonist. In this module, we’re going to explore techniques for writing a strong antagonist, how to make him, her or it a real, multidimensional character. (26:00)
Conflict Types
Conflict in a story is everything – it defines the very purpose of the protagonist. We can divide the types of conflict into one of several categories – each category helping to define the antagonist’s role in the story. They are man vs. man, man vs. self, man vs. society, man vs. nature and man vs. the supernatural. So in this module, we’re going to explore these various types of conflict and how you can use them to craft a compelling antagonist. (30:47)
Supporting Characters
A movie is populated with dozens of other characters – many of whom have an influence on the protagonist and the antagonist. These supporting characters either help or hinder, compliment or compete with our protagonist and antagonist. They add vibrancy and excitement to the story, all while serving as a valuable literary tool for you as you write the screenplay. In this module, we’re going to explore the function of supporting characters. (31:52)
Character Archetypes
All characters can be broken down into eight different archtypes – now these are the basic ingredients of creating a character, so of course you can mix and match them to create more complex, unique characters. But every supporting character fulfills one of more of these roles. The eight archtypes are the protagonist and the antagonist, Reason, Emotion, The Sidekick, The Skeptic, the Guardian and the Contagonist. So, in this module, we’re going to explore the six archetypes that make up supporting characters.
Designing Personality and Building Backstory
The act of writing is much more than simply creating characters – it’s about writing real people with real fears, ambitions, strengths and weaknesses. Although you need to be able to create real, believable people, every choice you make when creating them needs to support the story. Who they are helps them confront the plot, learn more about themselves and ultimately succeed or fail. Their background gives them the tools and experienced they need to confront the conflict, and most importantly, their tragic flaw gives their story a personal arc. So, in this module, we’re going to discuss how to create personality and backstory. (29:06)
How to Write Natural Dialogue
One of producers’ biggest criticisms of a script is the weak, cliche dialogue. Learn how to make your script stand out with tight, engaging dialogue from working Hollywood experts. Emmy-winning Executive Producer of “Everybody Loves Raymond,” Steve Skrovan, Writer/Producer Mike Emanuel, Writer John Anderson, Writer/Script Doctor David Freeman and Emmy-winning Director Jason Tomaric share valuable insight into avoiding cliches and writing tight dialogue. (21:46)
Section 4: The Writing Process
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
Title, Theme, and Log Lines
The title, theme, and log line are often the first exposure audience, producers, and agents may have to your story. But as a writing tool, they help you develop the plot thread and the heart of your story. In this lesson, we’re going to explore techniques for crafting a compelling title, developing a theme, and honing the log line to your screenplay. (15:02)
How to Write a Treatment and Outline
The treatment and outline for a movie is literally the backbone of the story, and the quality of your work in this phase can either make or break your script. Learn how to write an effective treatment and outline and simplify the process of writing the first draft. Working Hollywood writers teach you how to get the most out of this valuable writing tool. (19:30)
How to Format a Screenplay
Learn how to properly write and format the first draft of your script. This module is a complete guide that walks you through every step of how to format a screenplay. (18:13)
How to Write the First Draft
Now that your treatment and outline are complete, you can start writing the first draft of the script. This process is when you take each story beat and develop the action and dialogue of each scene. It’s a tedious process, and one that can be frustrating, but we will give you tips on how to make the first draft the best it can possibly be. (10:34)
Improve Your Rewrites
Once the first draft of your script is ready, the real work begins. Learn what to look for in the rewriting process, how to identify problem areas that may adversely affect the story and how to get the most out of each plot, character and line of dialogue. Emmy-winning Executive Producer of “Everybody Loves Raymond,” Steve Skrovan, Writer/Producer Mike Emanuel, Writer John Anderson, Writer/Script Doctor David Freeman, Emmy-winning Director Jason Tomaric and Jerrol LeBaron, president of the script brokerage site, inktip.com share industry tips and techniques on how to effectively rewrite your script. (13:55)
How to Market Your Screenplay
You’ve finished the script, now what? Working Hollywood writers and producers take you through the process of finding an agent or manager. Should you approach a producer instead? How do you deal with the studio Hollywood Reader? How do you cope with rejection? This module takes you through the intricacies of the Hollywood system and how to manage them. (21:18)
Your Screenplay and the Real World
Congratulations! Your screenplay is finished… or is it? When you sell or option your screenplay, agents, managers, and producers will often ask for multiple rewrites. In this lesson, we’ll show you how to manage feedback, how to protect your screenplay, grow your network, and improve your skills. (17:28)
Section 5: How to Use Final Draft Software
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
Final Draft - Script Basics
Learn the basics of script formatting and how you can use Final Draft software to begin formatting your screenplay, including scene headers, action lines, dialogue, parentheticals, dual dialogue, and transitions. (26:05)
Final Draft - Using Templates
Learn how to use existing templates to format your Final Draft script into hundreds of popular formats including sitcoms, hour-long dramas, SNL skits, multi-camera shows, Broadway musicals, and novels. (13:02)
Final Draft - Story Organizing
Learn how to throw away the old note card and use Final Draft’s story organizing capabilities to organize your scenes, characters, and dialogue in an efficient way. (15:21)
Final Draft - Distributing Your Script
Learn how to export and distribute your script through Final Draft for both physical and electronic delivery, prepare your script for table reads, water mark, and learn about Final Draft on mobile devices. (17:37)
Final Draft - Tips, Tricks, and Utilities
Enhance your use of Final Draft with a number of tips and tricks. (28:00)
Final Draft - Production
Learn how to use Final Draft to manage script changes and revisions, how to lock pages, manage scene numbers, scene omissions and additions, and export reports that quickly analyze your script for production. (23:15)
Section 6: Professional Writing Tutorials
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
The Changing Landscape of Television
Television has evolved from being a 3-network based medium, broadcasting their shows to a TV set in your living room to a massive content network accessible on wide range of devices – from home theaters to the phone in your pocket. Just as the technology has evolved, so too has the way stories are written to accommodate these new viewing habits. In this engaging FilmTalk, Emmy-nominated writer Pamela Douglas reveals incredible techniques for adapting your writing style for the new age of television. (34:36)
How to Become a Hollywood Writer
Emmy-nominated writer Pamela Douglas walks you through each step of how to begin your Hollywood writing career. Culminated from years of experience, Pamela’s insights give you an insiders perspective on how to build a successful career. (43:01)
Defining Comedy
When you think about comedy, what comes to mind? Slapstick, jokes, laughing? Well, comedy is much deeper and is a reflection on who we are as humans. In this FilmTalk, accomplished comedian Steve Kaplan provides shocking insight into comedy and how it relates to the human condition (29:36)
The Hidden Tools of Comedy
Comedy is often mistaken as being easy to write, act, and direct, but it may be one of the most difficult genres in which to work. In this brilliant FilmTalk, Steve Kaplan takes us on a journey into the hidden rolls of comedy to help us better understand what’s funny. (32:02)
Working in a Television Writer’s Room
Episodic television series hire a group of writers who work together to develop the character and story arcs, create the story lines, and write the scripts for every episode. Lead by the showrunner, the writers come together in what Hollywood calls “the writers’ room.” This collaborative workspace can be as politically-charged as it is creative and knowing how to work in the writers’ room can be the difference between a lucrative career and sitting on your couch. In this engaging FilmTalk, Emmy-winning writer Steve Skrovan takes us into one of the most creative rooms in the industry and shows you how to succeed in it. (24:40)

Producing
The film industry is a business, and while art is important, students learn the importance of the business side of filmmaking. Emmy and Academy Award winning producers walk you through every step of how to produce a film, including financing, unions, vendors, and liability protection.
Section 1: Development
Discover how the studio system works, the life-cycle of a script, and how the business and art of filmmaking intersect.
The Studio System
In this module, you’ll explore the studio system, learn who the players are, who the mini-majors are, the ever-evolving role of the studios as new corporate conglomerates, the types of movies they are making, and how you can be part of it. (32:38)
Working for a Studio
Learn how to get your project through the studio approval system, what studio executives are looking for, and how studios work with directors and producers. (26:05)
Making a Business Plan
Learn, step-by-step, how to build a business plan that will appease even the savviest investors. Hollywood producers take you through the process so you can go into the fund raising process confident in the movie you’re selling. (28:56)
The Reality Television Story Process
We have all seen reality programming on television, but what happens behind the scenes? Veteran reality producer Troy DeVolld takes into the fascinating world of reality production, its challenges, and the process of keeping the audience gripped in the drama of its characters. (22:22)
Packaging Your Movie
Learn how to choose the right actors for your movie, work with distributors in the development process, determine the value of your creative talent, how to attract top-tier talent, and ultimately make your movie attractive to distributors and audiences. (28:41)
Agents and Managers
Learn the different between an agent and a manager, the roles each fulfill, how to get one, the costs involved, and how to use their services to promote your career. (23:16
Section 2: Producing
The film industry is a business, and while art is important, learn the importance of the business side of filmmaking. Emmy and Academy Award winning producers walk you through every step of how to produce a film, including financing, unions, vendors, and liability protection.
Forming a Production Company
Learn how to choose the right corporate structure, set up a company, open the proper accounts, establish the legal framework for the production, work with an attorney, and set-up the production office. (32:54)
Raising Money
Learn how money is raised for motion pictures, from equity and debt financing to tax incentives. (39:30)
Tax Incentives
Learn how to take advantage of tax incentives, the difference between rebates and credits, how to convert credits into money, what to expect during the auditing process, and how to collect your money. (21:54)
Hiring the Crew
Learn how to hire an experienced crew, work with above the line vs. below the line, union vs. non-union crew members, manage pay-or-play deals, work with independent contractors and employees, address personal conflicts on set, and ultimately assemble the most talented professionals for your project. (30:31)
Managing Money
Learn to manage the budget, set-up a bank account, manage the flow of money throughout the production including payroll, loan outs, kit fees, per diems, mileage, and petty cash. (36:07)
Working with Vendors
Learn to find qualified vendors in your shooting area, manage relationships with vendors, the financial workflow from purchase orders to invoices, and tips to making sure you get the resources you need on set (18:34)
Unions and Guilds
Learn how the unions function, the benefits for members, the key unions: IATSE, DGA, SAG, and WGA, the differences in hiring union and non-union crew, how productions flip, and how to shoot in a “Right-to-Work” state. (35:40)
SAG-AFTRA
Learn how SAG functions, the ramifications of the SAG-AFTRA merger, how signatories work, how the Taft-Hartley act admits new members into SAG-AFTRA, and the benefits and drawbacks of Financial Core. Be prepared when working with SAG-AFTRA actors on your production. (25:47)
Production Insurance
Learn how to insure your production against liabilities and costs incurred from accidents, the types of insurance you’ll need, where you can buy production insurance, the costs of insuring a production, cast insurance, film and video tape insurance, equipment insurance, and E&O insurance. (19:54)
Scheduling and Budgeting
In this engaging series, learn how to balance the business of filmmaking with the art through effectively breaking down the shooting script, developing a realistic shooting schedule, and how to develop and manage an accurate budget.

Breaking Down the Script
Learn to properly break down the script, line the script, techniques for breaking down each scene, how to use scene breakdown forms, and how assistant directors and line producers should manage the breakdowns from other departments on the project. (19:54)

Scheduling the Production
Learn to determine the number of shooting days needed to shoot your film, how to determine the shooting order, manage day and night shoots, account for turnaround time, and the benefits of shooting consecutive shooting days. (33:54)
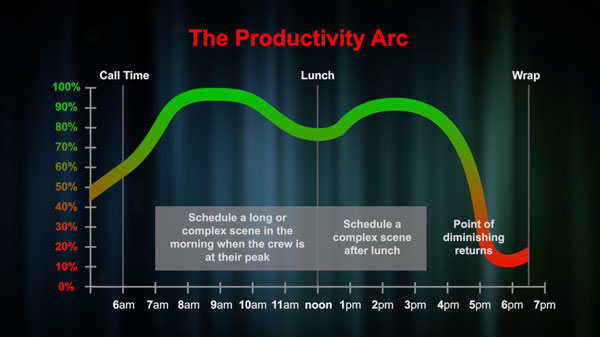
Scheduling the Shooting Day
Learn how to schedule company moves, meal breaks, learn the productivity arc of a shooting crew, how to work with the director’s shot list, skills for managing a shoot running over schedule, how to generate a one-line schedule, and how to create call sheets. (29:48)

Budgeting
Learn to create an accurate budget, tricks to reducing the budget if you’re running over, how to plan for contingencies, how to manage crew expectations, and how to go into production knowing you’ll have the money to finish. (30:45)

Crew Positions
There are a lot of craftspeople on a film set, and in this all new 23-part series, leading Hollywood crews from blockbuster TV shows and movies give you an in-depth look at each major below-the-line crew position.
The Producers
In this three lessons series, learn how the business managers of a film production work. From the line producer and unit production manager to the production coordinator, students get a detailed, inside look at the duties and responsibilities of the producers.



The Assistant Director Department
In this four lesson series, the Assistant Director team behind Titanic, Avatar, Stranger Things, and dozens of other Hollywood blockbusters teach you the day-to-day duties and responsibilities of the Assistant Director department, how to effectively manage the set, balancing the relationship between the director and producers, and how to get a job as an AD on a professional set.




The Script Supervisor
Working Hollywood script supervisors teach you the day-to-day duties and responsibilities of the script supervisor, how to interface with the director, the expectations of bridging the set to the editing room, how to effectively prep a production, and the expected deliverables when the production wraps.

The Camera Department
In this four lesson series, learn the roles and responsibilities of the camera department, from the moment to get the call for the job to the time they wrap. Working Hollywood camera crews reveal best practices, expectations, and responsibilities of a professional camera crew.




The Electric Department
In this three lesson series, professional Hollywood gaffers, best boy electrics, and electricians reveal the day-to-day duties and responsibilities of the electric department, how they interface with other departments on set, and how to make a living in the electric department.



The Grip Department
In this three lesson series, learn the job responsibilities of the group department and a professional production. Experienced, professional Hollywood grips methodically reveal the expectations of the grip department, how they interact with the electric department, the working hours and wages, and on-set practices to have a successful career in the grip department.



The Art Department
In this five lesson series, professional Hollywood production designers, art directors, set decorators, and property masters teach you the hierarchy of the art department, how to achieve the desired look within the schedule and budgetary limitations, and how to effectively interact with the rest of the crew.






Cinematography - Camera and Lens
In this comprehensive series, learn how the camera and lens work, and how to apply an understanding of the physics of cinematography to real-world on-set environments.
Focusing Techniques
From traditional focusing techniques of setting marks and measuring distances, to using digital focus assist tools, students learn how to set focus, overcome focus challenges, and proper on-set procedures.
Lens Focal Length
Students learn the power of the lens, how focal length affects the field of view and depth, changes in the illusion of time, plus how to work with zoom vs prime lenses, and compensate for crop factor.
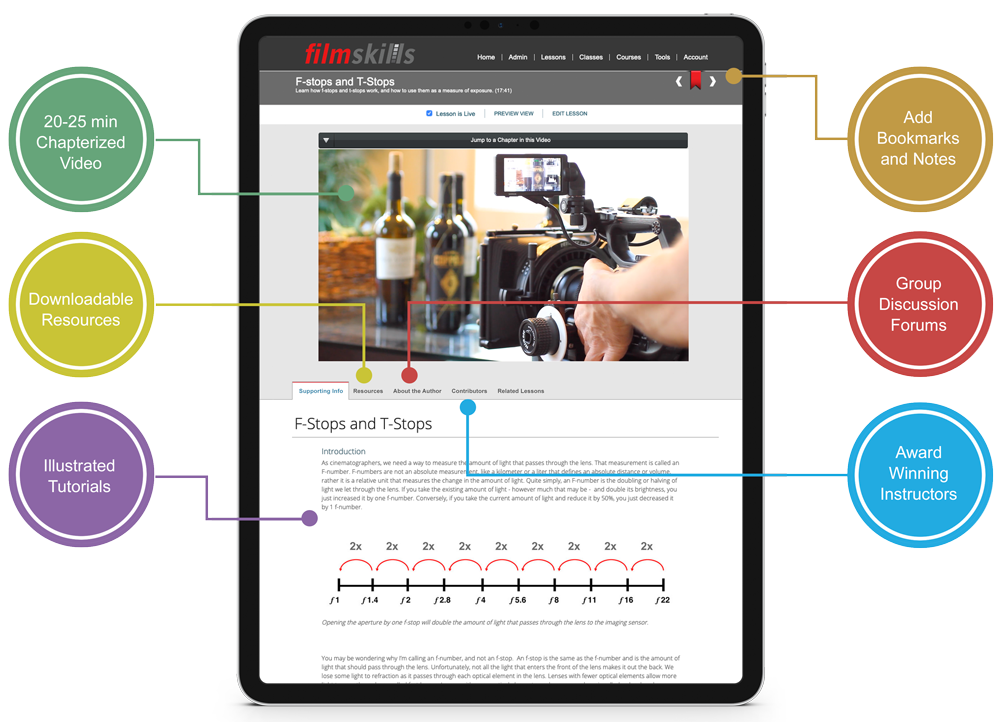
f-Stops and T-Stops
This lesson covers how f-stops and T-stops are used to determine exposure, how to work with fast and slow lenses, and how f-stops are used to determine camera exposure and lighting ratios on set.
Intro to Light and Exposure
Students are introduced to the nature of light, how it’s measured, and the foundations of exposure. Complex techniques of the inverse square law, dynamic range, latitude, and contrast ratios are made simple.
Taking Care of Lenses
Students learn how to properly change lenses, remove dust and debris, protect lenses both in transit and on set, prevent condensation, and how to properly clean the imaging sensor.
Watch a free lesson from this series
The Camera Shutter
Learn how electronic shutters function, how to choose the shutter angle, global vs rolling shutters, motion blur, managing screen flicker, and how to compensate exposure.
Frame Rates
This lesson provides a comprehensive look at frame rates, interlaced vs progressive, time code, drop frame, 3:2 pull down, slow motion and time lapse, and how to calculate exposure with different frame rates.
How to Prep a Camera
Students learn how to prep the camera, matte box, follow focus, monitor, cables, batteries, media, and how to conduct lens calibration tests to ensure the camera works properly on set.
Imaging Sensor and ISO
Students learn how the imaging sensor, CCD and CMOS chips, and photosites function, plus Bayer pattern and debayering, CODECs and RAW formats, bit depths, ISO, image quality, and gain.
How to Expose a Shot
Students learn exposure techniques including zebra stripes, false color, waveform monitors, histograms, and light meters, plus how to expose skin tones, and work within the camera’s latitude and contrast ratio.
Tripods and Sliders
Learn about the equipment that can help you stabilize and support the camera. From tripods to jib arms, this module is an outstanding introduction to the gear filmmakers use to control their camera shots.
Watch a free lesson from this series
Depth of Field
Students learn how to control, measure, and creatively apply the depth of field to their shots. This lesson balances science with art, and includes several demonstrations that show how the depth of field alters the emotion of the scene. (27:29)
- How to change the depth of field
- How to adjust the aperture and maintain exposure
- How distance from the camera affects the depth of field
- Circle of confusion and how it is calculated
- Measuring the depth of field and applying calculations on set
- How to choose the depth of field most appropriate to the content of the scene
Shooting Green Screen
The all-new video tutorial methodically guides students through the process of lighting, exposing, and recording green screen footage. (25:22)
- When to choose green or blue
- Differences between chromakey and digital blue/green
- Shooting in a studio vs on location
- How to light green screen (space lights, cyc lights, LED, Kino-Flo, book lights)
- How the bit depth and compression affect a key
- Capturing in LOG vs REC709
- How to expose actors
- How to reduce spill and create a cleaner key
Cinematography - Lighting
Go on set with Emmy and Academy Award-winning cinematographers as they teach you the art and craft of cinema lighting. Learn the tools used in creating, shaping, and softening light to achieve the look you want on set.

Section 1: Lighting Tools
Learn how to use professional lighting gear, when to choose the right light, and the benefits and limitations of each one.
Tungsten Lighting
Learn how to work with, operate and trouble shoot tungsten lighting fixtures. (11:48)
HMI Lighting
Learn about HMI light fixtures, how to operate, maintain and troubleshoot them. (19:22)
Kino-Flo Lighting
Learn how to properly use Kino-Flo lighting fixtures, ballasts, bulbs, and accessories on set. (14:20)
LED Lighting
New LED technology is appearing on sets around the world. Learn how LED lighting can add to your lighting toolbox. (7:10)
Low Budget Lighting Tools
Lighting equipment can be expensive, or unavailable. In this module, we’re going to show you simple, inexpensive lighting options for your shoot. (9:37)
How to Build a Light Kit
Light kits are self-contained, portable lighting kits. In this module, you will learn how to build a light kit, the pricing options and additional tools we’d recommend you always have on set. (15:31)
Section 2: Lighting Techniques
Learn professional techniques for creating, crafting, shaping, and softening light for perfects results.
Creating Soft Light
In this in-depth tutorial, students learn how to create soft light using a variety of techniques. (26:50)
- How to control the size of a light source
- Using Fresnels to craft the spread of light
- Controlling wraparound
- Working with diffusion on barn doors
- Working with soft boxes and Chimeras
- Skinning 4x4s
- Working with 6×6 overheads
- How to control spill from soft light sources
- Real world demo
Techniques to Reduce Light
The all-new video tutorial methodically guides students through the tools and techniques used to reduce light on your subject. (26:43)
- Working with wire scrims
- Working with dimmers
- Remotable Wi-Fi dimming options
- Solids, cutters, and floppies
- Creating negative fill
- Lensers and Courtesies
- Protecting fabric scrims
- Scrim and C-stand rigging safety
- Neutral Density gel on windows
Techniques to Shape Light
Creating light is easy – the art of lighting is in how the light is shaped. In this lesson, students experience industry-standard techniques to shape light to create the desired look. (23:53)
- The power of shadows
- Creating internal vs external shadows
- Benefits and drawbacks of barn doors
- Working with black wrap
- Egg crates and louvres
- Flags and solids
- Creating gobos
- Working with a cucoloris and brancholoris
- Building duvatyne skirts
Working with Reflected Light
While the previous lessons teach direct lighting techniques, this lesson shows students techniques on how to work with bounced and reflected light. (19:18)
- Factoring in the Inverse Square Law
- Foam core and bead board
- Collapsible reflectors
- Shiny boards
- Physics of reflected light
- Bouncing light off ceiling
- Working with overheads
- Shaping hair lights
- Working with mirrors
Watch a free lesson from this series
Color Temperatures and White Balance
The all-new video tutorial introduced students to color theory, how color is rendered on screen, and how common light sources appear on screen. (26:22)
- Defining how a camera sees white
- The Kelvin scale – origins and how it’s used
- How the imaging sensor sees color
- Measuring light sources with a spectrometer
- White balancing techniques
- How to cheat white balance
Attributes of Light
Learn the basic attributes of light and how to craft it to achieve the ideal cinematic look. (34:02)
Working with Mixed Light
From gelling lights to working with variable-color temperature LEDs, students learn how to color balance lights on set to achieve the desired look. This lesson covers:
- How to use gels to color correct light sources
- Light loss calculations through gels
- Working with LEDs
- Working with sunlight
- How to gel windows
Lighting a Scene
Learn how to assess an existing location, scene blocking and existing lighting to determine the best way to light a set. (24:42)
Lighting Outside
Learn how to light actors outside using only sunlight, reflectors and diffusion. (23:10)
Lighting People
Learn how to use the three-point lighting system to properly light people. (23:36)
Key Light Techniques
Learn advanced techniques for shaping your actor’s key light (25:20)
Advanced Lighting Techniques
Learn advanced lighting techniques to add style and quality to your shot (17:15)
Section 3: On-Set Lighting Tutorials
In this brand-new 9 part series, go on location to learn the practical approach to cinematography, how to identify and overcome common production challenges, and how to achieve a professional, cinematic look.
Daytime Interior - Kitchen Counter
Learn how to address exposure issues when shooting on location with windows, how to gel windows, balance exposure, and create natural, motivated lighting.
Nighttime Interior - Living Room - Morning
In this on-location tutorial, students learn how to create a morning light on a nighttime set. From working with haze and creating volumetric light, students learn to block and light for a cinematic look.
Nighttime Interior - Bedroom
In this tutorial, students learn to shoot a realistic night scene that achieves the desired emotional tone, all while producing a clean, noise-free image.
Daytime Interior - Kitchen Table Parts I & II
One of the most common scenes in a student production is the interior dialogue scene. Students learn how to address exposure issues when shooting on location with windows, how to gel windows, balance exposure, and create natural, motivated lighting.
Nighttime Interior - Kitchen Table
Students learn how to shoot a nighttime dialogue scene between two people, on location. Covering both his and her shots, this tutorial guides students through the blocking, composition, and lighting decisions behind creating a cinematic night scene.
Daytime Interior - Bedroom
Students learn how to create a sculpted light in a bedroom interior during the day. In this lesson, students learn how to balance exposure between the subject and outside sunlight, all while creating a cinematic look.
Nighttime Interior - Living Room
In this lesson, students learn how to light and shoot a scene with practical light fixtures, how to enhance the light so it is motivated, and how to bring the outside into the latitude of the camera.
Daytime Interior - Bathroom
Shooting in a small, confined space like a bathroom creates a range of production challenges, which we systematically address in this engaging tutorial. From a simple bathroom to a dramatic shot, students learn how to achieve the desired look on set.
Watch a free lesson from this series
Section 5: Grip and Rigging
In this series, we introduce students to the grip and rigging gear commonly used on set, proper rigging techniques, safety standards, and life on set as a grip.
C-Stands
C-stands are one of the most commonly-used stands on set. In this module, students learn about the different types of C-stands, how to use them and C-stand safety. (20:27)
Stands
From baby and combo stands, to hi-his and low boys, students learn how to safety use industry-standard stands on set. (16:37)
Knots for On Set Rigging
Students learn the most common rigging knots used on set and how to safely tie them.
Doly and Track
Dynamic camera moves can add production value to practically any shoot. One of the most common ways of moving the camera is to lay down track and use a camera dolly. This module introduces students to the common doorway dolly, shows you how to set-it up and use it. (12:54)
Clamps
Students learn how to safely use mafers, cardellinis, C-clamps, furniture clamps, playtpus clamps, scissor clamps, gaffer grip, safe rigging safety. (23:36)
Grip Support
Students learn how to properly use apple boxes, sand bags, furniture pads, and taco carts on real-world sets. (8:02)
Grip Tools
Learn basic tools used by grips on set, including essential personal tools every grip is expected to have. (9:20)

Directing
Go on set with Emmy and Academy Award-winning cinematographers as they teach you the art and craft of cinema lighting. Learn the tools used in creating, shaping, and softening light to achieve the look you want on set.
Section 1: Director's Craft
Designed to help you understand the director’s role in visual storytelling, the seven updated lessons combine interviews with Hollywood directors, on-set tutorials, and methodical step-by-step approach to the director’s process.
A Director’s Prep - Beginning a Project
Learn how to begin the directing process, read the script for the first time, best prepare long before you even set foot on set, and how to breakdown the script for character and story. (27:17)
Creating a Shot List
Learn how to create a shot list, location requirements, how to decide your shots, the elements in a shotlist, how the shot lists are used to schedule and budget a film, and to prepare for days when you go over schedule or over budget. (17:41)
Basic Coverage
Learn the basic template for shooting the action in a scene - the master, coverage, inserts and cat-in-the-window shots, learn how to vary shot size to increase coverage, break the standard, plan for the edit, and ensure you get the coverage you need. (21:45)
Advanced Coverage
Learn how to craft a oner, create a psychological impact for each shot, create compelling establishing shots, manipulate the pacing and rhythm of a scene, determine the opening visual, and enhance transitions from one scene to the next. (25:54)
Watch a free lesson from this series
Storyboards and Pre-Visualization
Learn how to work with a storyboard artist, use pre-visualization software, know how detailed storyboards should be, creative restrictions to be aware of, how to create storyboards even if you can’t draw, and when to use animatics. (30:47)
Continuity and Script Notes
Learn the importance of on-set continutiy, how to maintain it, the role of the script supervisor, and how to create an industry-standard continuity notebook. (22:12)
The Visual Story
Learn how to use visual elements of shape, space, line, color, rhythm, movement and tone to frame the story. (38:22)
How to Shoot a Scene
Learn the process of how to shoot a scene: block, light, rehearse, tweak, and shoot. (39:23)
How to Direct a Scene
Emmy-winning director Jason Tomaric applies the concepts in this series to a sample scene, in which he walks students through the process of directing, blocking, and shooting a short scene. (31:00)
Working with the Military
Learn how to approach the National Guard, work with the US military, the types of resources the military can provide, and how to work with reenacters. (20:23)
Section 2: Casting the Roles
Learn how to find and cast actors who bring a creative presence to the screen and provide a marketable face for distributors and audiences.
Finding Actors
Learn how to work with casting directors to approach recognizable actors, how to develop a script that appeals to certain talent, the art of packaging, casting actors on your own, and the pros and cons of working with unknowns. (23:25)
How to Conduct an Audition
Learn how to find the ideal audition space, attract qualified actors, conduct auditions, and learn what to look for so you can find the perfect cast for your movie. (25:09)
The Art of Auditioning
Auditions can be an intimidating and difficult process for both actors and directors. In this FilmTalk, accomplished actor Michael Laskin takes us into the actor’s process to reveal tips and techniques for honing and improving the audition process. (18:38)
Callbacks
Learn how to conduct the second and third auditions, what to do after the auditions, recognize danger signs in actors, and how to prepare the actors for the next step: the rehearsals. (12:08)
Working with Local Celebrities
Learn the best way to approach local celebrities, how to use them, and the secret benefits they can bring to your movie. Working with local celebrities will not only improve the visibility of your production, but lead to a number of other benefits that can not only help promote the movie, but assist greatly in production. (15:46)
Section 3: Directing Actors
Learn the skills to effectively direct actors to achieve an authentic performance on set.
Analyzing Character
In this module, you will learn directing techniques to help actors determine the subtext, intent, and back story of their characters. Develop your directing skills and help your actors portray honest, memorable characters. (30:19)
Rehearsing Actors
Learn how to structure rehearsals, how to conduct a table read, and what the responsibilities are of the director and actors during the rehearsal process. (26:47)
Directing Actors on Set
Learn what to say to an actor at the beginning of every scene – 30 seconds before you call action and 30 seconds after you call cut, learn how to rehearse on set, establish strong blocking, and how to help actors balance their performance with the technicalities of film production. (38:28)
The Language of Directing Actors
Learn from Hollywood actors and directors on how to approach and work effectively with actors on set, how to deal with problematic actors, and how to communicate in the actor’s language. (34:07)
Watch a free lesson from this series
Blocking the Actors
Learn how to block the actors, what story cues to look for, how to drive the blocking emotionally, and how to work with the actors to get the best physical performance possible. (33:11)
Directing Extras
Learn how to find extras, the right way to direct them, how to cheat them on set, liability concerns and how to avoid them, logistics on the shooting day, and the most common problems filmmakers encounter when working with extras. (24:35)
Directing Mistakes
Learn to identify common directing problems and how to fix them to ensure you get the best performance on set possible. (26:28)
Rehearsal Exercises
Learn valuable techniques from working Hollywood directors to get to the heart of the actors’ performance, learn rehearsal techniques from developing the character to overcoming mental blocks on the set. (12:49)

Production Design
Learn how to shape a convincing world around your characters that reveals their personalities, all while creating a realism that transcends disbelief. From the art of set design and creating the look, to the craft of set construction, you will learn every facet of the production design process from leading Hollywood filmmakers.
Set Design
Learn how to design a set so it fulfills both the technical and artistic needs of the production. Whether you have a budget or not, this module reveals tips and tricks of designing a great set.
Set Construction
Hollywood sets look vast and amazing on screen, but in reality, they are built as minimally as possible to achieve the look. What appears as stone, marble, wood, glass and brick may in reality by plywood flats, Styrofoam, textured facades and exquisite paint jobs that give the illusion of richer materials. In this module, you will learn how to construct a movie set, from building flats to painting and texturing the walls to building a floor and ceiling. (39:15)
Set Dressing
Most constructed sets are empty rooms, void of life and character. Set decorators bring in everything from rugs and drapes to items on surfaces, artwork on the walls, and anything the actors do not touch. The quality of the set dressing not only adds to the visual impact of the frame, but to the characters themselves. This module takes you inside the set decorating process, on a tour of a Hollywood prop house, and gives you dozens of tips and techniques for dressing your set, whether it’s on a sound stage or a real location. (33:17)
Props
Props are any object an actor physically touches. If an actor doesn’t touch it, technically the object is part of the set dressing. In this module, we’re going to look at props, how to identify, build, gather and use them to best tell the story..
Creating The Look
Movie sets don’t appear out of nowhere, but are the result of a very careful collaboration between the art department and the director. In this module, you will learn the steps that go into creating an environment from the pre-production meeting to budgeting to researching a look. (32:10)
Tour a Prop House
Take a walk through Lenny Marvin's Prop Heaven in Burbank to see the props used in today's movies and TV shows.

Production on Location
The majority of film productions are shot on location, which means the film crew must interact with location owners and the general public. In this series, viewers learn the process of scouting and securing a location, working with location owners, and managing the public.
Finding Locations
Locations play a critical role in every film production, and in this module you will learn how to properly break down the script, scout locations, work on cold scouts, and how to assess the technical feasibility of a location and its local industry support. (18:51)
Film Commissions
Each state has a film commission tasked with attracting motion picture production to that state. In this module, learn the services offered by a film commission, how to use their services to find the best location for your movie, liaise with local industry, and potential unexpected issues.
Working with Location Owners
Approaching and asking a location owner to use his or her property for your film shoot can be a daunting task. In this module, you will not only learn how to approach a location owner, but which contracts and forms are needed, proper protocol, how to deal with problems and how to help a location owner prepare himself for the whirlwind that is the production process. (34:02)
Film Permits
In most major cities, you’re required to obtain a permit to be able to shoot on both public and private property. This module will walk you through the permitting process, when one is required, how to get one, the costs involved and common traps associated with free permits. (24:33)
Location Tech Scouting
Movies are either shot on a sound stage or on a real location. Shooting on location can bring its share of challenges, which is why understanding how to do a thorough site survey is critical to being prepared. In this module you will learn what to look for when you’re scouting locations. (26:03)
Community Relations
No one makes a movie in a vacuum - every day you shoot will invariably affect someone, whether it’s one neighbor or an entire community. In this module you will learn how your film shoot affects the public, how to work with local officials, how to notify residents, how to leave a positive impact on the community when you’re finished shooting and a general code of conduct for crews when shooting on location. (26:41)
Watch a free lesson from this series

Production Life - Working on Set
Get first-hand advice from working filmmakers on proper on-set behavior and etiquette, from what to wear and how to prepare for a day shooting, to how to properly use walkie talkies and manage a range of personality types.
A Day on Set
Get a glimpse into a typical day on set, how to prepare yourself for the on-set experience, and what you can expect to find when working on a film crew.
Filmmaker’s Toolkit
Film sets are places of uncertainty where anything can happen, and sometimes having a $2 tool can save you from disaster. But being prepared is a matter of experience, and we’re going to share with you the experiences of professional filmmakers who want to save your shoot from disaster. In this lesson, students learn how to create a kit with the necessary tools, gadgets, and gizmos to help the set run smoothly. (10:40)
Proper Set Etiquette and Behavior
Movie sets are a unique work environment. Each crew consists of freelancers who may have never met before, all coming together to tame an unseen location to make movie magic. The dynamics, personalities, egos, and stress of production make navigating the politics of the movie set intimidating to new filmmakers. In this lesson, veteran Hollywood filmmakers share their insights on how to handle yourself on a movie set. (15:44)
Walkie Talkie Etiquette
Walkie talkies are the primary tool for keeping a film crew in constant communication. The language and techniques for using a walkie talkie on set is different than other industries, and knowing how will help you look more professional on set. In this lesson, you will learn proper walkie talkie technique. (14:59)
What to Bring to Set
Working on set is about being prepared with the right clothes and tools to take on any situation. In this lesson, we will show you how to properly dress for a day working on set, the tools you need to bring, and tips for making your work day just a little easier. (9:31)
Working with Difficult Personalities
Hollywood is full of amazing people - artists, technicians, craftsmen, executives, performers, and business execs. Each of these people have their own personalities - some more challenging than others. Part of surviving in the industry is knowing how to work with everyone - including the most difficult personalities. Hollywood veteran Casey Slade shares with us his entertaining insights on how to deal with ego in the film industry. (22:56)

Audio Recording
Experience the step-by step approach to recording high-quality audio on set, from choosing the right microphones to learning how to use a boom mic. Leading audio experts including the head of Apple Audio and inventor of THX Tom Holman, teach skills they learned over a lifetime career
The Physics of Sound
In this module we’re going to look at the physics of sound – the sound wave, how it can be measured and ultimately, how it is used to create emotion through story. (26:01)
Audio Pre-Production
Learn how to prepare for a shoot by breaking down the script, determining the best equipment to use and how to address complex scenes. (24:52)
How Microphones Work
Microphones convert sound energy into electrical energy and can do so in different ways. You will learn how microphones capture sound, how that sound is converted into energy and the strengths and weaknesses of each microphone type. (23:52)
Microphone Pick-Up Pattern
Learn the different types of pick-up patterns, how they capture sound, and which to choose when recording audio. We will explore omnidirectional, cardioid, hypercardiod, figure-of-8, multipattern mics and much more. (19:10)
The Microphone Boom
The boom mic is one of the most common ways to record good on-set audio. In this module you will learn how to choose the proper boom pole, the various types of shock mounts and wind reduction tools. Recording excellent audio begins with having the right tools. (19:09)
Boom Operating Techniques
At first glance, the boom mic seems to be fairly simple and straightforward to operate. In actuality, however, it is a very tricky skill which balances the ideal mic placement with the movements of the operator. So in this module, we’re going to look at proper technique for using a boom pole to record on-set audio. (23:02)
Watch a free lesson from this series
Location Recording Techniques
Recording location sound is a challenging process - and the decisions you make on set can either make the post-production process easy, or can cost tens of thousands of dollars. In this lesson, we’re going to look at how to properly prepare for a shoot - the type of gear you’ll need, how to conduct a location scout and tips for minimizing location noise. (28:17)
Lavalier Microphones
Lavalier mics are small condenser microphones that can be worn on the body or hidden on set. In this module, we’re going to look at the various types of lavalier microphones, how best to use them and their limitations. (20:33)
Recording the Audio
Once the microphone picks-up sound, it is then encoded into either an analog or digital signal, then recorded to a device. With advancements in technology, the quality of the recorded signal can be virtually indistinguishable from the original sound. In this module, we explore how sound is recorded and encoded. (37:58)
Audio Configurations
Audio can be recorded many ways - directly into the camera, through a mixer, and/or to a separate recording device. In this module, you will learn common techniques for recording sound, how to manage line/mic level inputs, work with dumb and smart slates, and work with timecode. (23:35)
Cables and Adapters
It’s so easy to focus on the specifications and quality of both the microphone and the recording device that you forget about the cables that connect them. Cables, although seemingly the least interesting equipment, can make or break your shoot. In this module, we’re going to look at the types of cables, and connectors, when to use them and how to care for them. (21:16)

Documentary Filmmaking
Learn the entire documentary story-telling process from over a dozens leading documentary filmmakers. From developing the story through on-set production techniques, the documentary storytelling process comes alive.
The Documentary Format
In this lesson, students learn about documentary storytelling, the types of documentaries, the challenges of the medium, the difference between objective and subjective filmmaking, observational cinema, and how the documentary format differs from fictional movies. (17:05)
Documentary Story-Telling Tools
In this lesson, we explore the story-telling tools of the documentarian. We dive into how interview, B-roll, recreations, and archival footage can be used to support the story you are telling. (23:01)
Finding the Story
In this lesson, students learn how to find the story by refining the subject matter, develop a viable and engaging hypothesis, unlock the secrets of the story arc, find a balance between the art and commerce of documentary filmmaking, know the audience, and narrow down broad concepts. (24:50)
Preparing the Interview
Learn how to find qualified subjects, techniques for preparing to shoot the perfect interview, tips on what to wear, how to select the right chair, how to work through a translator, and how to deal with release forms – especially in a heated or controversial interview. (33:03)
The Art of the Interview
Learn how to warm up a nervous subject, how to determine the objective of the interview, the first question you should always ask, how to uncover the truth especially with subjects intent on deceiving or leading you, how to work with difficult subjects, how to conduct interviews in which you are also on camera, and how to conduct man-on-the-street interviews. (27:18)
Ethics and Objectivity
Learn the difference between a subjective and objective approach to filmmaking, how to recognize bias, how to balance your own ethics and feelings in difficult situations, and ethical guidelines both in the field and in the editing room. (21:37)
Documentary Pre-Production
Learn how to effectively prep a documentary shoot, research your subject, properly use release forms and secure permissions to protect yourself legally, know what crew to hire, and how to determine when it’s time to shoot. (18:51)
Choosing the Gear
Learn how to prepare for life in the field, how to choose the right camera and camera support gear, how to manage batteries and media on location, how to prepare for audio recording, how to pack for the road, and how to make sure your gear survives airports and the airlines. (32:08)
The Interview Location
Learn what to look for in potential locations, how to work in the all-too-common hotel room or conference room, how to make sure a space is rights-cleared, and how to create a comfortable environment for your subject. (18:53)
Interview Camera Set-Ups
Learn how to shoot interviews alone with one camera, one camera with an operator, a cross-shooting two-camera technique, how to work with different frame sizes, work with monitors, techniques for shooting on the run, and how and when to use auto settings. (25:05)
Shooting B-Roll Footage
Learn to harness the power of B-Roll for your film, how to use verité footage, basic coverage techniques in the field, how to shoot sequences, how to tailor B-roll for interviews, and how to shoot B-roll after the edit. (21:52)
Field Shooting Techniques
Learn when to shoot in auto or manual modes, how to properly shoot your coverage, how to adjust the amount of footage for the project, how to shoot green screen plates, how to work with ambient sound, and how to manage the legalities of a shoot. (20:17)
Editing Documentaries
Learn how to manage your footage, organize interviews and B-roll, how to find and narrow the story, how to maintain your objectivity in the thick of the process, know what to cut, and how to finish the film. (28:41)

Safety Training
Introducing a comprehensive safety training program based on the California Safety Pass program and taught be several of its instructors. Designed to increase on-set safety awareness and reduce liability, students learn industry best safety practices.
Safety is an Attitude
This module covers individual crew member responsibility towards safety, how human factors contribute to accidents and how they can be prevented. Students learn actions on how to create a safe environment on set. (20:27)
On-Set Safety
Students learn to conduct safety meetings, proper clothing, drug and alcohol policies, safety bulletins, and how to maintain an organized set. Students learn the fundamental principles of creating a working safe environment. (34:55)
Studio Facilities Safety
Students learn how to maintain a safe environment when working on a soundstage - from maintaining fire lanes and working from a height, to working with combustible materials and maintaining a safety protocol. (19:42)
Lighting Equipment Safety
Lighting Equipment Safety (24:23) From high-output lights and dimmer boards, to HMIs and working with light stands, this module covers the hazards and safe practices of working with lights and electrical equipment. (24:23)
Location Safety
Students learn how to assess the hazards of a location - from environmental to animal hazards. We discuss how to work safely alone, how to safely work on rooftops, around the public, and how to make a location safe for production personnel. (18:51)
Electrical Safety I
Students learn how electricity and circuits work, about proper grounding and polarity, and how little electricity is needed to electrocute an adult. This module reveals how to map the circuits in a location and calculate safe loads, and what happens when power demands exceed the internal wiring of a structure. (32:19)
Electrical Safety II
Working around high voltage wires can, and has been, deadly. In this module, students learn proper guidelines for working around high voltage power sources, how to spot faulty equipment and correctly use cords and outlets, including in high-traffic areas. Students learn about the risks, and effects of electric shocks, electrocution, electric fires and how to prevent them. In addition to preventative measures, this module covers emergency medical procedures in the event of shock or electrocution. (22:28)
Vehicle and Roadway Safety
This module teaches students proper safety protocol for working around public roadways, when the road is used in the scene, or the crew is shooting near a roadway. (16:37)
Shooting in Moving Vehicles
Students learn proper safety procedures when shooting driving scenes on a public street - from the poor-man’s process to process trailers, this module covers every aspect of what to do and what not to do. (20:12)
Grip and Rigging Safety
Students learn proper rigging safety techniques - from hanging overhead lights and properly securing a 12x12 in a breeze, to proper knots, securing stands, and ensuring all rigs are safe on set. (25:34)
Vehicles, Lifts, and Tools
Students learn the safety procedures for working with hand power tools, ladder and scaffold safety, the safe operation of truck lift gates and aerial lifts, and how to work around production vehicles. (18:49)
Weapons and Props
A dangerous and frequent problem in film schools is the improper use of prop weapons, which can be illegal and deadly. In this module, students learn how to properly use weapons (and prop weapons) on camera, from handling procedures, to employing a qualified armorer, to dealing with the public and working with local officials. (25:13)
Pyrotechnics and Special Effects
This module explores the proper and safe procedures for working with squibs, explosives, fire, smoke and fog, and other types of atmospheric effects. Students learn the dangers of working with pyrotechnics, the proper permitting process and how to hire an experienced, trained pyrotechnician. (23:51)
Environmental Safety
Students learn how to recognize, prepare for, and work in various environmental situations - from shooting in extreme heat to extreme cold, to working around water and in locations where there may be health hazards. Students learn how to recognize and react to symptoms of heat stroke and frost bite, unstable structures and locations with airborne contaminants. (27:27)

Post Production
The editors, sound mixers, and composers guide you through the process of post production, including editing for story, mixing the audio, scoring the scene.
Section 1: The Art of Editing
Emmy-winning television and film editors take students inside the process and psychology of film editing. Learn how to properly shoot footage on set to maximize options in the editing room, when to cut from one shot to the next, how to choose your shot selection, how to work with the editor, and how to create the most emotion in each scene.
Hiring an Editor
In this module, you will learn how to find a qualified editor, how to assess an editor’s demo reel, tips for ensuring his vision and communication style match yours, and how to ultimately get the best person for the job. (11:22)
Working with an Editor
Learn techniques for communicating your vision to the editor, the editor’s workflow, and what you can do to get the best results possible in the editing room. (20:23)
Concepts of Editing
Learn when to cut, how to determine whether you should cut or not, the hierarchy of story-telling importance when editing, what to show or not show, and how to use psychology to craft a scene the invokes powerful emotions – all through how it is edited. (37:39)
Data Management and Workflow
Learn how to develop a system for organizing the footage from set to post, how to develop a workflow that keeps the process smooth and conflict-free, how to conduct post-production meetings, the role of the post-production supervisor, standard techniques for labeling and managing footage, and data handling techniques. (26:39(
The Assembly Cut
Learn how to approach the assembly cut, how to manage music and sound effects, what should or shouldn’t be included, and how to address issues of pacing, story, and character development. (21:33)
Stock Footage
Learn how to use stock footage, how to understand a licensing agreement, where to find stock footage, how to manage the technical requirements, and what your rights are when distributing your production. (20:58)
Editing a Dialogue Scene
Learn the correct and incorrect ways of shooting dialogue on set, advanced techniques for manipulating the pacing and emotional intensity of the scene, how to work with changing background ambience, techniques for balancing the visual performance with the dialogue, how to mix the audio, ultimately how to get the best performance through the edit. (34:27)
Editing Action
Learn how to edit action for proper flow, continuity, and pacing. Learn techniques for compressing time, revealing only the essentials to keep the story moving forward, and advanced editing techniques used by master editors. (21:51)
The Rough Cut
Learn how to approach the rough cut, determine what moments work, how to re-structure the story, and ultimately create a movie that stands on its own- divorced from the script. (19:04)
Test Screenings
Learn how to prepare for and conduct a test screening, how to choose the right test audience, what questions to ask after the test screening, and how to filter the responses into usable comments that can improve the story (21:34)
The Fine Cut
Learn techniques for perfecting every single frame of your movie before locking the picture edit, how you will know when the movie is done, the implications of locking the picture, and the process of prepping the film for audio. (14:44)
Online/Offline Editing
Learn how and when to work in an offline environment, how to transition to an online cut, and techniques for ensuring the process goes smoothly. (8:47)
Color Grading
Learn the color grading process, how it differs amongst formats, the balance between technical and artistic grading, how to protect yourself from the “fix-it-in-post” mentality, and how to get the look you want. (15:40)
Section 2: Audio Post-Production
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
Intro to Audio Post-Production
Learn the five components of audio and go to the sound studio to experience the construction of the audio for a scene. Learn the ADR process, the contributions of Foley to the mix, the role of sound effects, and ambience, and the music. (26:06)
ADR
One of the most important elements of the audio track is the dialogue - not only from the creative sense, but technically. The dialogue editors work hard to make sure the audience can hear the everything the actors are saying and that it’s free and clean of any background noise or distracting sounds. While dialogue editors may try hard to remove the background noise, or even smooth it out, sometimes there is no other option than to re-record the dialogue. This process is called Automated Dialogue Replacement (ADR), and in this module you’re going to learn the process of properly using ADR to improve the quality of your dialogue track. (30:31)
Directing Actors in ADR
Learn how to work with actors to get the best vocal performance possible during the ADR process, address acting problems and actor fatigue, and gain valuable tips on how to direct a natural and realistic performance so the ADR performance becomes better than the original delivery on set. (28:19)
Foley
Learn how Foley is recorded and mixed to create a full, rich audio track. Learn the types of Foley, how much should be recorded, the process of recording Foley, and how to properly schedule and budget this creatively demanding aspect of audio post-production. (33:33)
Sound Effects
Learn the process of creating a compelling sound effects track for your movie, where to find high quality sound effects, how sounds effects and Foley work together, how to find a balance with the dialogue and music, and the role of the sound effects editor. (24:49)
Mixing the Audio
Throughout the audio post-production process, each department - dialogue, Foley, sound effects, and music generate tens of thousands of individual sounds across hundreds of tracks. All of these sounds need to be mixed together into a single soundtrack - whether it’s a stereo track for broadcast, a 5.1 mix, or a 10.1 theatrical mix. This process is called mixing the audio, and it happens on a dubbing stage. In this module, we’re going to explore the dubbing process and how all these audio elements get mixed together to create the sonic experience for the audience. (24:49)
Section 3: Music Composition
In this first section, learn how to get started by prepping your writing space, and identify a marketable idea.
The Emotion of Music
Music is as much of a performer in a scene as the actor or the camera. Its movements, tone, and intensity help shape the emotion of the moment. But, like any performance, the right performance can bring added life to the scene, but too much can overwhelm the moment, pulling the audience out of the story. In this module, you will learn how to balance music’s role in a movie against the other dramatic elements, tips and techniques for creating a compelling score that supports the emotion of the movie, and how to avoid overscoring. (28:25)
Working with a Composer
One of the most important collaborations on a movie happens between the director and the composer. The composer adds the final performance - the music - to the narrative tapestry, and understanding how that tapestry should be woven is why the director/composer relationship is so important. In this module, you’re going to experience the entire process of scoring a movie, from the initial meeting with the composer to the very end when you’re making the final tweaks to the music. Improve your communication with the composer, get the best score for your movie, and craft the best emotional ride for the audience. (47:33)
The Who and How of Music
Learn the people involved in crafting the score to a movie, the types of scores available, and how music is recorded - from synth to live instruments. (31:29)
Scoring the Scene
Award-winning composer, Chris First teaches you how to build a MIDI-based system by taking you on a tour through his own studio. He then walks you through his step-by-step approach to scoring a scene from the movie, “Clone.” Go inside the composer’s world and learn the process of how music is properly used to enrich a scene. Learn how to work with a composer and the composer’s process of writing original music for a movie. (18:23)
Music Licensing
Are you interested in using a popular song or existing soundtrack in your movie? Music - just like movies and books - is protected by copyright law, which restricts its usage to the owner of the copyright. In recent years, many record labels and studios have begun cracking down on illegal downloading and usage of their work, making the legal use of this music somewhat confusing for users. In this module we’re going to explore the legal way to license and use music for your movie. Protect yourself, respect the rights of the music artist, and learn how to properly license music for use in your production. (33:15)

Marketing and Distribution
From the birth of an idea to the green light, this series takes you inside the writing process, and teaches the complete process of writing a feature-length screenplay.
Section 1: Film Marketing
Professional Hollywood marketers from both the studios and independent world teach students how to effectively market their movies to investors, audiences, and distributors.
Film Marketing
Film marketing is the other half of a Hollywood movie’s budget. The cost of reaching an audience and getting them interested in seeing a specific title is an art and a science. In this lesson, you will learn how the film marketing machine in Hollywood works and how you can use it to market your movie. (15:41)
Reaching Your Audience
Before you can start building a marketing campaign, you have to know who your audience is. Every image, every color, every word, and every place you put your ads need to be strategically chosen to speak to the audience you want to attract. This is Marketing 101 - and it’s often the most overlooked part of a marketing campaign. In this lesson, we will show you how to determine your audience to craft the perfect marketing campaign for the best results. (26:05)
Designing the Key Art
First impressions, as the old cliché goes, are lasting. This couldn’t be more true than when talking about the movie poster. The movie poster is only one component of the marketing campaign and relies heavily on the “key art” for the film. Key art is the visual motif that defines the entire marketing look and feel, including images, fonts, and the color palette. The key art is used everywhere from social media ads to movie posters and is the first and most important marketing tool in gaining the interest of audience members, distributors and producers. In this module, you will learn techniques for designing effective key art. (16:11)
Making a Movie Trailer
The movie trailer is the most important marketing tool you have to sell your movie. Distributors have made deals on the trailer alone, which makes the look and feel of the trailer even more important than the movie itself. In this module, you will learn tips and techniques for creating an engaging trailer to properly represent your film. (27:23)
Building Your Website
One of the least expensive, yet most effective ways of marketing your movie is to set up a website. While you can make it as elaborate as you like, always think about the audience for the site - moviegoers who may want to see the film or distributors you are courting to buy the film. In this module, you will learn how to properly craft an effective site to market your movie. (5:43)
Building a Press Kit
When approaching television, radio, and newspapers to do a story about your movie, they will ask for a press release or an electronic press kit (EPK). This EPK provides journalists a variety of useful information, quotes, and photographs they can use to quickly and easily compose the story. In this module, you will learn how to craft an EPK for your film. (13:35)
Working with the Media
The film industry is more about marketing that it is about film production. The studios often spend more money on advertising, publicity and marketing than they do on producing the movie itself. While the same holds true in the independent filmmaking arena, few filmmakers can afford much more than a few hundred posters and a website. That makes media coverage a critical part of your marketing campaign. In this lesson, you will learn how to reach the media, how to conduct an effective interview, and how to get your message across. (17:56)
Section 2: Distribution
Learn how the Hollywood sales machine works from top producers and distributors at film festivals, markets, and online.
Introduction to Distribution
Learn how the distribution process works, the way studios approach the process, the windows and time frames of distribution, how to approach self-distribution, and knowing your audience. Guiding you through these tricky waters are veteran studio executives from LucasFilm, Sony, and FreeMantle Media. (23:35)
Film Ratings and the MPAA
The MPAA is responsible for issuing the ratings we see in a movie - G, PG, PG-13, R, and NC-17. The rating your film receives has a direct impact on the willingness of distributors to pick-up your film, and your film’s revenue potential. In this module, you will learn how the MPAA works, and how you can best prepare for a favorable rating. (14:09)
Domestic Distribution
Making the film is only one part of the process. Selling it is the other. Whereas making the movie has been a stressful process, the game of finding a distributor, negotiating the contracts, preparing the deliverables, and facing the sometimes staggering costs of E&O insurance, conversions, and M&E mixes hit most filmmakers by surprise. In this module, we will prepare you for the distribution process so you know what to expect, what materials are needed, and most importantly how to protect yourself in the high stakes game of film distribution. (24:14)
Foreign Distribution
Learn how foreign sales agents work, how to find a reputable agent, common scams used to steal your movie without paying you, what you will be expected to deliver, how to collect your money, and hundreds of other tips. We take you to the heart of it all at the American Film Market to see – firsthand, how the foreign distribution process works. (37:22)
Film Festivals
We all dream of an extravagant Sundance Film Festival premiere where we are showered with offers from anxious distributors stepping over each other to acquire our films. While this certainly happens, the reality is that film festivals offer much, much more in the way of contacts, self-promotion, and an opportunity to pitch your next project to investors and producers.In this module you will learn how to find a qualified producer’s rep, how to get into top film festivals, what to do once you are accepted, how to attract the right audiences at the screenings, and how to leverage the opportunity for your next production. (26:46)
Mistakes Filmmakers Make at Film Festivals
Getting into a film festival is an exciting accomplishment for any filmmaker, but how do you make the most of the opportunity? By properly positioning yourself and your movie, you can attract the interest of distributors, agents, managers, and producers. But if you don’t, you will have wasted an opportunity to further your career. (30:05)
Internet Distribution
The Internet has become a powerful alternative to traditional distribution outlets for independent filmmakers, but while this option seems alluring, it is fraught with challenges. Finding a voice and an audience online is a long and expensive road, and while the profit margins can be greater, so can the time and effort you put in for those profits. In this module you will learn how to properly distribute your movie online, how content aggregators work, how to find a unique presence online, and how to leverage your online movie to get your next movie deal. (27:26)












